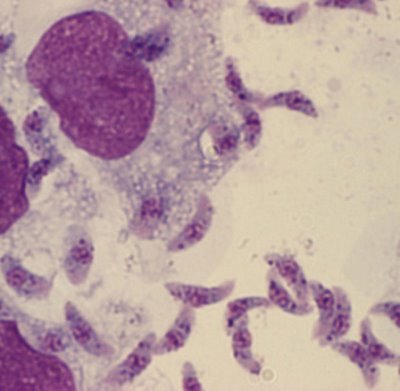
Toxoplasma gondii is a protozoan parasite that can cause serious problems in the fetus during pregnancy. It causes less serious problems in adults, but once infected you are infected forever with the parasite cysts living in your brain. That means if you are going to receive immunosuppressive therapy for cancer or transplantation treatment, you probably should get tested for toxoplasmosis. Above is a photomicrograph of the rapidly dividing 'tachyzoite' stage of the parasite. Some of the parasites are being taken up or invading a macrophage.
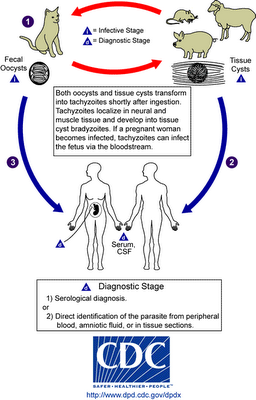
You become infected with toxoplasma primarily by eating poorly cooked meat although getting it directly from cat feces when changing the litter box can also happen. The life cycle of the parasite is above. The sexual cycle of the parasite life cycle takes place in the cat or other felines. The asexual stage occurs in almost any other warm blooded creature. 20% to well over 50% of some human populations are infected with T. gondii.
So what? Well, an interesting article has come to my attention through the Faculty of 1000. The title is "Women infected with parasite Toxoplasma have more sons." The work is out of Charles University in the Czech Republic. These researchers have reported that women infected with T. gondii have more sons than daughters, a lot more. For every 260 boys born, there are only 100 girls born to women infected with T. gondii. Even more interesting, this phenomenon correlates with high anti-T. gondii antibody levels.
The full text of the article can be found here.

1 comment:
I saw that article about a month ago - interesting stuff. I've also seen that some anthropologists have looked at a connection between rates of latent T gondii infection and culture - T gondii supposedly can have a mild affect (or "effect?") on behavior. Warm climates tend to have higher rates of infection, and are also known for more, erm, "boisterous" cultures.
Post a Comment